How to Build a Pallet Shed: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
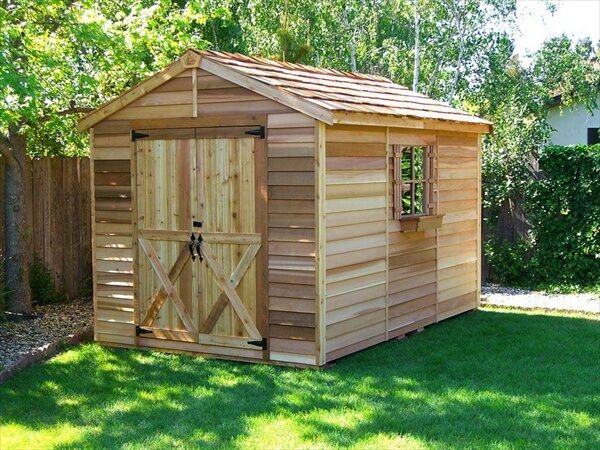
Constructing a pallet shed offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for additional storage space. This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step process for beginners, emphasizing safety and structural integrity. While utilizing reclaimed pallets presents inherent challenges, careful planning and execution can result in a sturdy and functional shed.
Phase 1: Planning and Preparation
The success of any construction project hinges on meticulous planning. This phase focuses on design, material acquisition, and site preparation.
1.1 Shed Design and Dimensions
Begin by defining the shed's purpose and desired dimensions. Consider the items to be stored and the available space on your property. Sketch a basic plan, noting the dimensions of the walls, roof, and door. A simple rectangular design is ideal for beginners. Accurate measurements are critical for a structurally sound shed.
1.2 Pallet Selection and Assessment
Sourcing suitable pallets is crucial. Inspect each pallet thoroughly for signs of damage, rot, or infestation. Prioritize pallets made of pressure-treated lumber for enhanced durability and pest resistance. Avoid pallets marked with the "HT" symbol (heat treated), as these may contain chemical treatments unsuitable for direct contact. Aim for pallets of consistent size and quality for easier assembly.
Calculate the approximate number of pallets needed based on your design. Remember to account for both the walls and the roof. It's advisable to have extra pallets on hand to account for potential damage or imperfections during construction.
1.3 Site Preparation and Foundation
Choose a level and well-drained location for your shed. Clear the area of vegetation, debris, and rocks. A stable foundation is paramount. Options include:
- Concrete Slab: Provides the most robust and level base, but requires more significant investment and preparation.
- Gravel Base: A simpler and less expensive option, involving laying a layer of compacted gravel to create a level surface.
- Wooden Skids or Sleepers: A cost-effective solution, requiring placement of treated timber on a leveled gravel base to elevate the shed and improve drainage.
The chosen foundation method will dictate the initial steps of the construction process.
Phase 2: Shed Construction
This phase details the assembly of the shed's walls, roof, and door.
2.1 Wall Construction
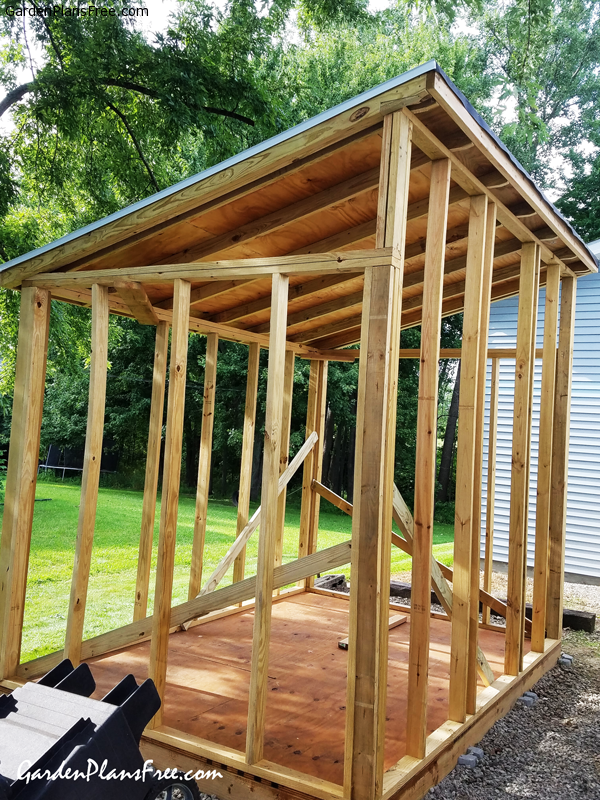
Begin by assembling the wall frames. This involves carefully connecting pallets vertically, ensuring they are aligned and securely fastened. Use appropriate screws or nails, considering the type of wood and the desired strength. Pre-drilling pilot holes is recommended to prevent wood splitting. For added stability, consider using additional bracing between pallets. Assemble at least two walls before moving onto the next steps.
2.2 Floor Construction
If not using a pre-existing concrete or gravel base, construct a wooden floor. This can be achieved using additional pallets laid flat and secured together. Ensure the floor is level and provides a stable base for the walls. For enhanced strength and durability, consider using plywood or OSB (Oriented Strand Board) sheeting over the pallets.
2.3 Wall Assembly and Securing
Once the walls are constructed, position them on the prepared foundation or floor. Use additional bracing or corner supports to ensure the walls remain square and plumb. Secure the walls together using screws or nails, ensuring a strong and stable structure. Consider using additional support beams or posts for added structural integrity, especially for taller sheds.
2.4 Roof Construction
The roof construction requires careful planning. A simple gable roof is recommended for beginners. This involves constructing two triangular roof sections using pallets laid at an angle. Secure the roof sections to the top of the walls using appropriate fasteners. Ensure the roof has sufficient overhang to protect the walls from rain and snow. Consider adding roofing felt or a similar water-resistant material for additional protection.
2.5 Door Installation
The door can be constructed using additional pallets or purchased separately. If constructing a door from pallets, ensure it is sturdy and securely hinged to the wall frame. Consider adding a latch or lock for security. The door placement should be planned during the wall construction phase.
Phase 3: Finishing Touches and Refinements
This phase focuses on enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of the shed.
3.1 Weatherproofing
Apply a weatherproofing treatment to protect the wood from the elements. This may involve using a wood sealant, paint, or stain. Ensure the chosen product is suitable for exterior use and provides adequate protection against moisture and UV radiation. Pay particular attention to the joints and seams to prevent water ingress.
3.2 Internal Finishing
Consider adding shelves or other internal features to maximize storage space. This can be achieved using additional pallets or other suitable materials. Ensure the internal finishing enhances the functionality and usability of the shed.
3.3 Safety Considerations
Always wear appropriate safety gear, including safety glasses, gloves, and sturdy footwear during construction. Use caution when handling power tools and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Dispose of waste materials responsibly and in accordance with local regulations.
Building a pallet shed is a rewarding project that allows for creativity and customization. By carefully following these steps and prioritizing safety, beginners can successfully construct a durable and functional storage solution. Remember that variations in pallet size and quality may require adjustments to the construction process. Always prioritize safety and structural integrity throughout the project.